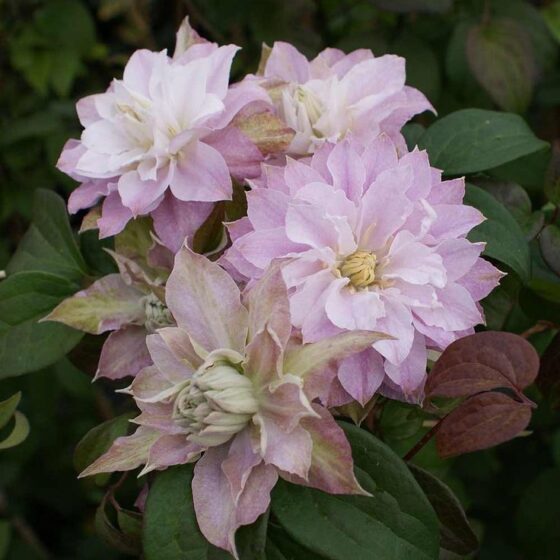
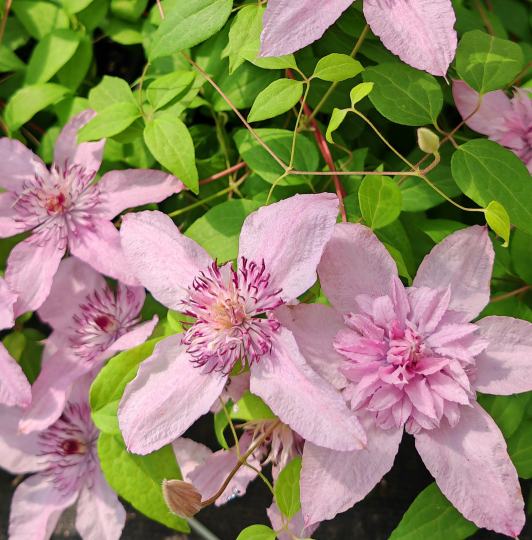
起源 & 传播: 苹果的主要祖先种群起源于中亚的天山山附近, 特别是在现代阿拉马地区, 哈萨克斯坦, 为所有现代苹果品种提供了基因池. 苹果通过早期贸易路线从中亚传播到世界其他地区, 例如丝绸之路.
植物描述: 苹果树是一棵落叶树,可以达到高度 15 仪表, 通常形成一个相对较短的圆顶冠. 它的叶子是椭圆形到椭圆形的, 沿着边缘的钝锯子装饰. 五月份北半球开花的苹果树, 随着果实期限从7月至10月延长.
气候要求 & 耕种: 苹果适应多种气候条件, 在35°至50°北部和南部的纬度地区蓬勃发展. 他们需要积累 1000 到 1600 加热单位和无霜期 120 到 180 确保水果成熟的日子. 传播技术包括嫁接, 分层, 种子播种, 和组织培养. 嫁接是最常见和有效的方法, 确保新植物保留父树的所有特征. 果园应在土壤深层层的地区建立, 充足的阳光, 和最小的污染. 适当的培养管理包括适当的修剪, 水和营养管理, 以及花和水果变薄,以促进健康的生长并提高产量和质量.
营养价值 & 健康益处: 苹果富含营养素,包括胡萝卜素, 维生素c, 矿物质 (例如钾, 磷, 镁, 钙), 和饮食纤维. 他们提供许多健康益处, 例如保护视力, 帮助预防心血管疾病, 并促进肠运动. 此外, 苹果含有多酚, 这可能有助于延迟衰老, 帮助预防癌症, 并提高免疫力.
问: 您的红血病植物适合我的气候区?
一个: 我们的铁线素品种在USDA野性区域繁荣发展 4-9. 最适合多样化的气候, 但是我们建议在购买前检查您的特定区域. 与您联系您的位置 - 我们建议您完美的品种!
问: 您如何确保植物在国际运输中生存?
一个: 我们发货 裸根的植物 休眠期间 (最佳运输) 使用专用包装:
✅水合根包装纸
✅通风箱
✅温度控制的物流 (如果需要)
植物准备好植物,并详细的适应说明.
问: 哪种红斑的品种盛开最长/最简单的生长?
一个: 对于初学者和延长的开花, 考虑:
• 长开花: Clematis 'Piilu' (重复开花), 'Jackmanii' (夏天)
• 维护低: 铁线莲 品种 (抗病性)
告诉我们您的目标 (容器/地面, 日晒) 用于个性化建议!
问: 您的最低订单数量是多少 (量) 用于批发?
一个: 标准量订单是 50 植物每种品种 (允许混合匹配). 对于首次购买者, 我们提供 样本顺序 10-20 植物 测试质量. *查询大量折扣 200+ 单位!
确保您的红血病状况良好, 全世界
🌟关键保证
"98% 生存率保证"
我们运送休眠的裸根植物 (十月 - 五月) 使用科学支持的方法. 如果植物到达损坏, 我们提供免费的替代品 - 无需额外的费用. [查看担保条款]
📍 我们的4步包装过程 (国际运输的理想选择)
步 1: 休眠时间
自然休眠期间的收获植物 (最佳无应力运输).
步 2: 根水合
包裹在保湿凝胶中的根 + 潮湿的泥炭苔藓以防止脱水 30+ 天.
步 3: 防震包装
✅透气袋 (防止霉菌)
✅自定义纸板管 (保护茎)
✅标记的绝缘盒 "活植物 - 远离热量"
步 4: 合规准备
包包括:
• 植物检疫证书 (符合ISPM-15)
• 海关声明 (准确的植物描述)
• 多语言护理指南 (种植/适应)
🌐全球交付选项
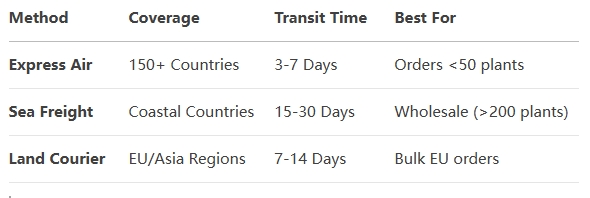
✦实时跟踪: 接收气道芭比娃娃号码 + 发货时门户链接.
❄️气候控制解决方案
我们根据目的地气候量身定制包装:
• 寒冷地区: 绝缘 + 加热包 (对于-10°C至0°C)
• 热带地区: 通风盒 + 水分控制包
•与我们联系以获取极端气候解决方案 (沙漠/北极)
⚠️买家的重要笔记
1. 货运通知: 我们电子邮件 3 派遣前几天确认地址.
2. 海关职责: 负责当地进口税的买方 (我们提供完整的文档以简化许可).
3. 植物健康: 可能会发生轻微的叶子滴/枯萎 - 植物在适当的水合下恢复48h.
💡 客户的提示
冬季订购 (nov-dec) 下个赛季最好的根源!
选择海运 200+ 植物 - 节省 60% vs. 空运!
📞 需要紧急帮助?
点击: 联系我们 - 来自中国的Lanxiu园艺领先的Clematis股票供应商